Search keywords:
product name, product type, model number,
test method, manufacturer, technique, application
Fuel Cell Porometer
BACKStandards:
Applications:
The performance of many fuel cell components is determined primarily by the characteristics of the pore structure. Flow of reactants and products is determined by the pore size and pore distribution of electrodes, wide range of gas humidity found in many applications can change the pore structure, components subjected to compressive stress during operation can considerably modify the pore size, pore structure of each layer of multilayer composites often used as fuel cell components can determine the performance of the fuel cell, and reaction rate of reactants is governed by the surface area of through pores. The Fuel Cell Porometer is designed to measure all the relevant pore structure characteristics of fuel cell components.
Product Information:
Introduction
Principles
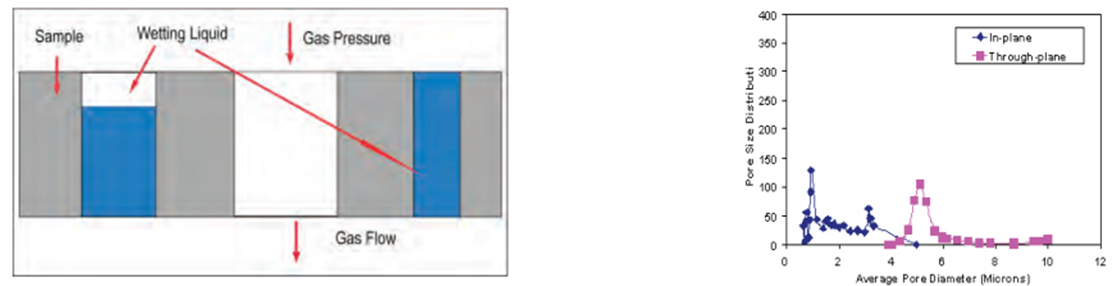
Principle of the Fuel Cell Porometer Principle of the Fuel Cell Porometer
Features
Unique features
◆ Characteristics measureable using gas with 0 to 100 % humidity
◆ Test temperatures can be 200°C and in special situations 800°C
◆ Pore size measured in samples under compressive stress of up to 1000 psi
◆ Pore structure of each layer of a multilayer composite
◆ Pore diameters down to about 0.013 µm
Features
Measured flow rates through dry and wet samples with increasing di erential pressures are used to compute many characteristics:
◆ Pore throat diameters Pore distribution
◆ Largest pore throat diameter Gas Permeability
◆ Mean flow pore diameter Through pore (envelope) surface area
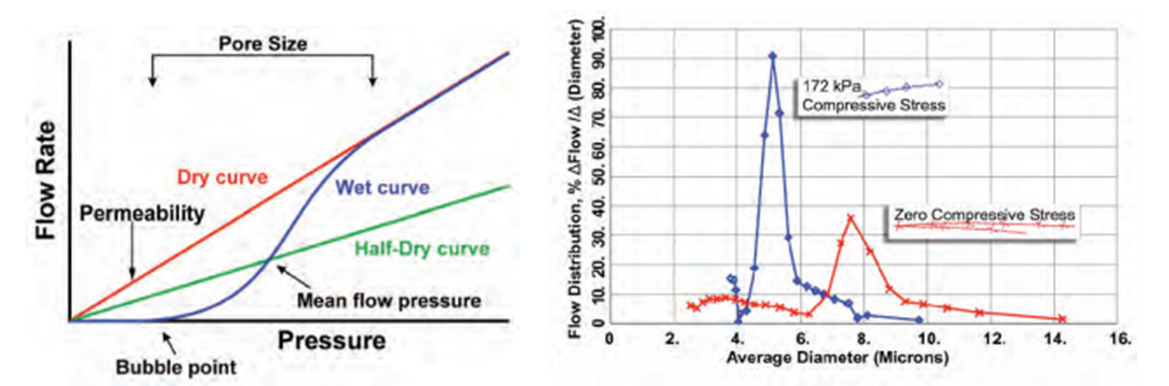
Flow Rate/Pressure Graph Flow Distribution Graph