Search keywords:
product name, product type, model number,
test method, manufacturer, technique, application
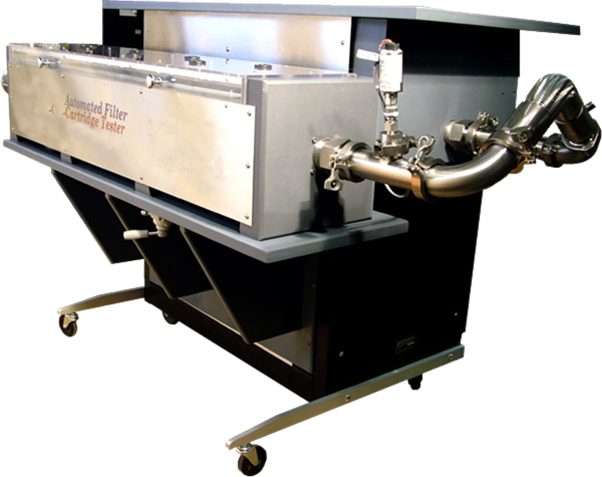
Automated Filter Catridge Tester
BACKStandards:
Applications:
Product Information:
Introduction
Fully assembled filter cartridges are widely used in many industries including biotechnology, pharma ceutical, chemical, beverage, and food. Filtration efficiency in all these applications is determined by the pore structure of the complete filter cartridge. The Filter Cartridge Analyzer measures the bubble point, the mean flow pore diameter, and the pore distribution of the complete cartridge rather than a small sample of the filter media. The tester also measures the gas permeability.
Principle
A wetting liquid is allowed to spontaneously fill the pores of the cartridge and air pressure is increased to empty pores and permit gas flow. Measured differential gas pressure and flow rates through a cartridge in wet and dry conditions yield various pore structure characteristics.
D = 4γ1 cosθ1 /p
Where:
D= Pore Diameter
γ1 = Interfacial Surface Tension of Wetting Liquid
cosθ1 = Contact Angle of the Liquid
p= Differential Gas Pressure
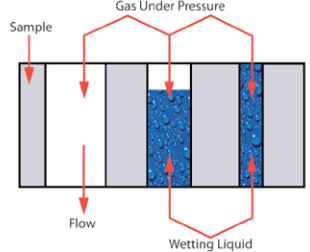
Instrument
The unique instrument design easily deals with very high volume of gas flowing through large cartridges and reduces pressure drop by eliminating narrow ducts, bends and constrictions. A tank for storage of gas under pressure sufficient for the test is supplied as part of the test equipment so that standard laboratory air supply is adequate for test execution. The sample chamber holds the cartridge between a fixed head and an adjustable head. By adjusting the position of the adjustable head cartridge of any length can be accommodated. A pneumatically operated piston applies sufficient pressure to seal the edges of the cartridge.
Capability
Pore Diameter: The measured differential gas pressure yields the through pore throat diameter.
Bubble Point: Computed from pressure for initiation of flow through wet sample.
Mean Flow Pore Diameter: Computed from mean flow pressure at which wet curve and half-dry curves meet.
Pore Distribution: Given in terms of distribution function, f.f=-d[(Fw/Fd)x100]/dD where Fw and Fd are wet and dry flow respectively.
Gas Permeability: Computed from the gas flow rates using Darcy’s Law.
Feature
Completely automated.
Windows based software, simple operation, and minimal operator involvement.Bubble Point: Computed from pressure for initiation of flow through wet sample.
Mean Flow Pore Diameter: Computed from mean flow pressure at which wet curve and half-dry curves meet.
Pore Distribution: Given in terms of distribution function, f.f=-d[(Fw/Fd)x100]/dD where Fw and Fd are wet and dry flow respectively.
Gas Permeability: Computed from the gas flow rates using Darcy’s Law.
Feature
Completely automated.
Only a few minutes for test execution Sintered metal, woven metal, polymeric, and ceramic cartridges can be tested.
Adequate safety precautions.
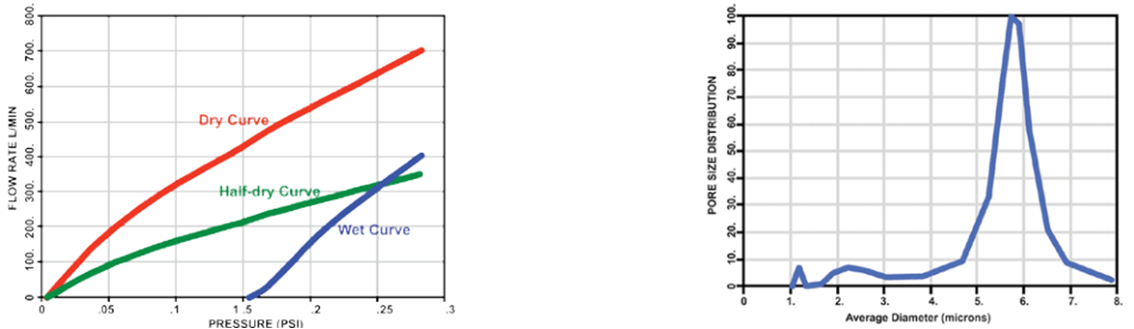
Change in Flow Rate Compared to Change in Pressure Pore Size Distribution